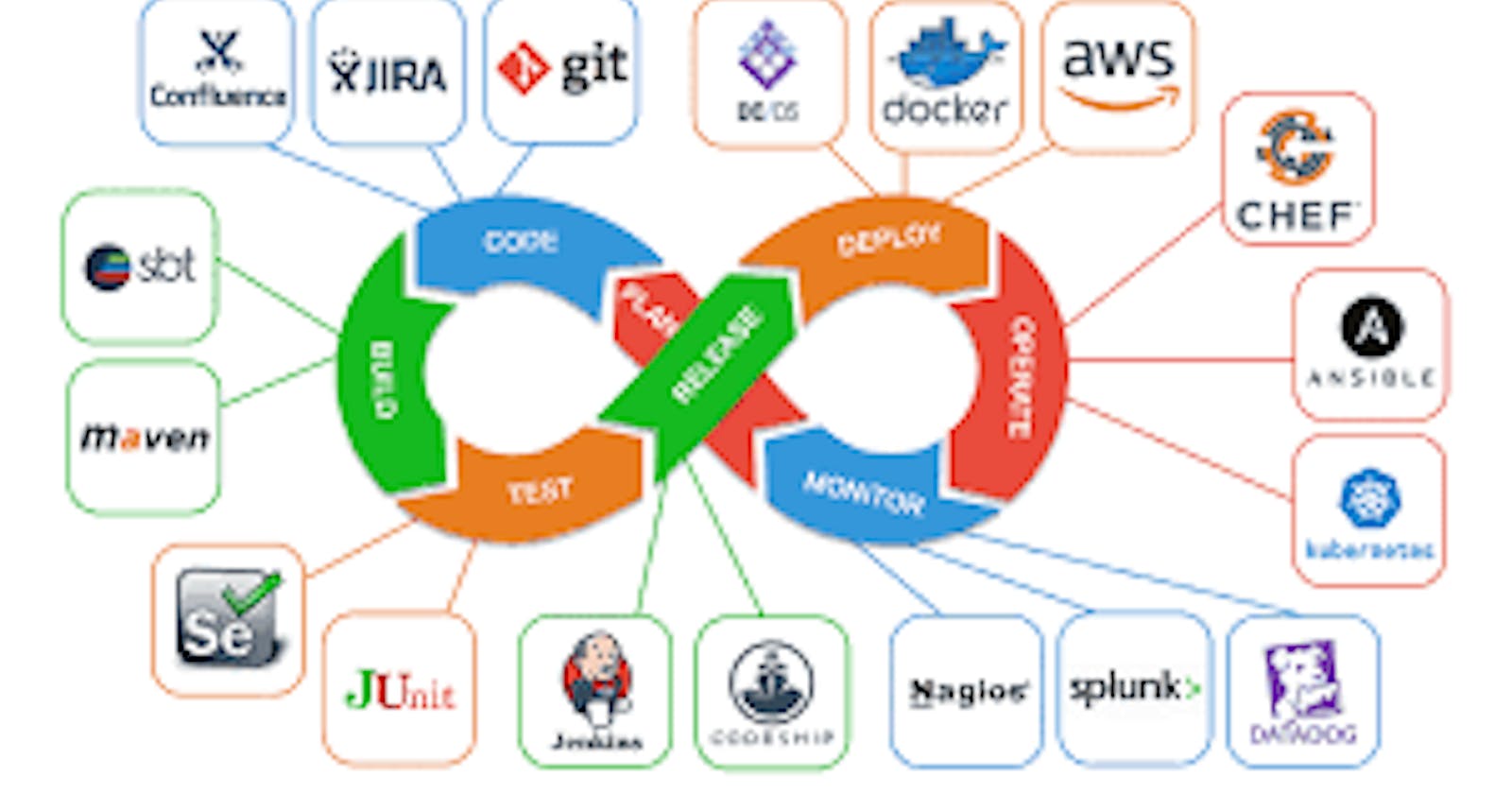
Comprehensive Overview of Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Introduction: Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) are crucial practices in modern software development, aiming to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and speed of the software delivery pipeline. CI/CD is a set of principles and practices that enable developers to deliver high-quality software at a rapid pace while minimizing manual intervention. This writeup provides an in-depth understanding of CI/CD, its key components, benefits, and best practices.
Continuous Integration (CI):
CI is a development practice where developers regularly merge their code changes into a shared repository, followed by an automated build and testing process.
The primary goal is to detect integration issues early in the development cycle, ensuring that the codebase remains in a working state.
CI reduces the risk of bugs and conflicts by automating the compilation, testing, and validation of code changes.
Continuous Deployment (CD):
CD extends the CI process by automating the deployment of code changes to production environments.
The goal is to deliver software updates to end-users as quickly and reliably as possible.
CD includes continuous delivery (automated deployment to a staging or pre-production environment) and continuous deployment (automated deployment to production).
Key Components of CI/CD:
Version Control System (VCS): Central to CI/CD, VCS (e.g., Git) allows developers to track changes, collaborate, and manage code versions efficiently.
Automated Builds: CI systems (e.g., Jenkins, Travis CI) automatically compile source code, ensuring that it can be successfully built without errors.
Automated Testing: Comprehensive test suites (unit, integration, and acceptance tests) are executed automatically to validate the correctness and functionality of the code.
Artifact Repositories: CI/CD pipelines often produce artifacts (compiled binaries, deployable packages), which are stored in repositories for later use in deployment.
Benefits of CI/CD:
Faster Time to Market: Automation accelerates the software delivery process, allowing new features and bug fixes to reach users quickly.
Improved Code Quality: Early detection of integration issues and automated testing contribute to higher code quality and reliability.
Reduced Manual Errors: Automation minimizes the risk of human errors during the build, test, and deployment phases.
Enhanced Collaboration: CI/CD fosters collaboration among development, testing, and operations teams by providing a consistent and automated process.
Best Practices:
Small, Frequent Commits: Break down work into small, manageable units to facilitate frequent integration and testing.
Automated Testing: Maintain a robust suite of automated tests to ensure code stability and catch regressions.
Immutable Infrastructure: Treat infrastructure as code, enabling reproducibility and consistency across different environments.
Monitoring and Logging: Implement monitoring and logging to detect and diagnose issues in real-time.
Challenges and Considerations:
Security Concerns: Automated pipelines should include security checks to identify and address vulnerabilities.
Cultural Shift: Adopting CI/CD may require a cultural shift in the development team to embrace automation and collaboration.
Complexity: As CI/CD pipelines grow, managing and maintaining them can become complex, necessitating proper documentation and version control.
Conclusion: Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment are pivotal practices in the modern software development landscape, promoting collaboration, efficiency, and high-quality software delivery. By automating key aspects of the development lifecycle, CI/CD enables organizations to respond rapidly to market changes and deliver reliable software to users. Embracing CI/CD practices is not only a technical decision but a cultural shift that fosters collaboration and innovation in software development teams.